sklearn-GridSearchCV & hyperopt & hyperopt-sklearn 调参
目录
- sklearn-GridSearchCV
- hyperopt
- hyperopt-sklearn
sklearn-GridSearchCV
常用参数
sklearn.model_selection.GridSearchCV
| 参数 | 含义 | 其他 |
|---|---|---|
| estimator | 所使用的模型 | 假定这是scikit-learn中模型接口。该模型可以提供score方法或scoring参数 |
| param_grid | dict或list | 带有参数名称作为键的字典,例如param_grid=param_test, param_test={'n_estimators': range(1, 6)} |
| scoring | 评价标准,默认为None | 字符串,或是可调用对象,需要其函数形式如:score(estimator, X, y);如果是None,则使用estimator的误差估计函数 |
| cv | 交叉验证参数,默认为None,使用三折交叉验证 | 整数指定交叉验证折数,也可以是交叉验证生成器 |
| refit | 默认为True | 在搜索参数结束后,用最佳参数结果再次fit一遍全部数据集 |
| iid | 默认为True | 默认为各个样本fold概率分布一致,误差估计为所有样本之和,而非各个fold的平均 |
| verbose | 默认为0 | 日志冗长度。0:不输出训练过程;1:偶尔输出;>1:对每个子模型都输出 |
| n_jobs | 并行数,int类型 | -1:跟CPU核数一致; 1:默认值 |
| pre_dispatch | 指定总共分发的并行任务数 | 当n_jobs大于1时,数据将在每个运行点进行复制,这可能导致OOM,而设置pre_dispatch参数,则可以预先划分总共的job数量,使数据最多被复制pre_dispatch次 |
scikit-learn内置可用评价标准如下:scikit-learn model_evalution
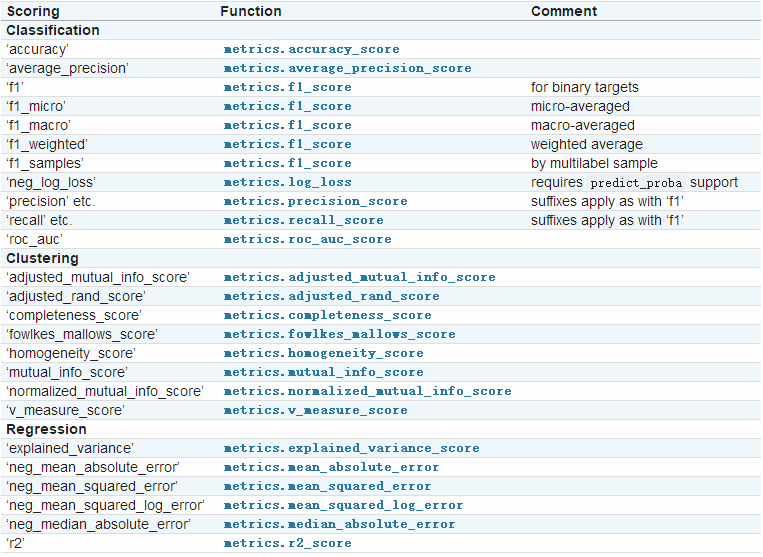
常用方法
| 方法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| grid.fit() | 运行网格搜索 |
| grid.grid_scores_ | 给出不同参数情况下的评价结果 |
| grid.best_params_ | 已取得最佳结果的参数的组合 |
| grid.best_score_ | 优化过程期间观察到的最好的评分 |
代码
1 | # coding:utf-8 |
hyperopt
Hyheropt四个重要的因素:
- 指定需要最小化的函数(the objective function to minimize);
- 搜索的空间(the space over which to search);
- 采样的数据集(trails database)(可选);
- 搜索的算法(可选)
目标函数,指定最小化的函数,比如要最小化函数\( q(x,y) = x^2 + y^2 \)
搜索的算法,即hyperopt的fmin函数的algo参数的取值。 当前支持的算法有随机搜索(hyperopt.rand.suggest),模拟退火(hyperopt.anneal.suggest),TPE算法。
搜索(参数)空间设置,例如优化函数q,输入 fmin(q,space=hp.uniform(‘a’,0,1))。 hp.uniform函数的第一个参数是标签,每个超参数在参数空间内必须具有独一无二的标签。 hp.uniform指定了参数的分布。
其他的参数分布:
- hp.choice返回一个选项,选项可以是list或者tuple.options可以是嵌套的表达式,用于组成条件参数。
- hp.pchoice(label,p_options)以一定的概率返回一个p_options的一个选项。这个选项使得函数在搜索过程中对每个选项的可能性不均匀。
- hp.uniform(label,low,high)参数在low和high之间均匀分布。
- hp.quniform(label,low,high,q),参数的取值是round(uniform(low,high)/q)*q,适用于那些离散的取值。
- hp.loguniform(label,low,high)绘制exp(uniform(low,high)),变量的取值范围是[exp(low),exp(high)]
- hp.randint(label,upper) 返回一个在[0,upper)前闭后开的区间内的随机整数。
搜索空间可以含有list和dictionary。
1
2
3
4
5from hyperopt import hp
list_space = [hp.uniform('a', 0, 1), hp.loguniform('b', 0, 1)]
tuple_space = (hp.uniform('a', 0, 1), hp.loguniform('b', 0, 1))
dict_space = {'a': hp.uniform('a', 0, 1), 'b': hp.loguniform('b', 0, 1)}
sample函数在参数空间内采样
1 | from hyperopt import hp |
简单的例子
1 | from hyperopt import fmin, hp, tpe |
Perceptron鸢尾花例子
使用感知器判别鸢尾花,使用的学习率是0.1,迭代40次得到了一个测试集上正确率为82%的结果;使用hyperopt优化参数,将正确率提升到了91%。
1 | # coding:utf-8 |
结果
由于使用tpe搜索算法,每次搜索的结果都不一样,不稳定。
1 | =============== before tune =============== |
xgboost癌症例子
1 | # coding:utf-8 |
结果
1 | train_x: (455, 30) test_x: (114, 30) train_y: (455,) test_y: (114,) |
hyperopt-sklearn
目前hyperopt-sklearn只支持部分Classifiers\Regressors\Preprocessing,具体请见上面hyperopt-sklearn的Github主页。
安装
1 | git clone git@github.com:hyperopt/hyperopt-sklearn.git |
使用模版
1 | from hpsklearn import HyperoptEstimator, svc |
鸢尾花例子
1 | # coding:utf-8 |
MNIST例子
1 | # coding:utf-8 |
参考
>